MEMS Sensor Drift Suppression
Drift is a major problem for MEMS inertial sensors. Gyroscope and accelerometer outputs are integrated to calculate the position in navigation applications. Sensor drift leads to unacceptable errors in navigation. Our research is focused on inertial sensor drift supression with on-chip stress sensors.
We integrate stress sensors with MEMS gyroscope to calibrate its drift.
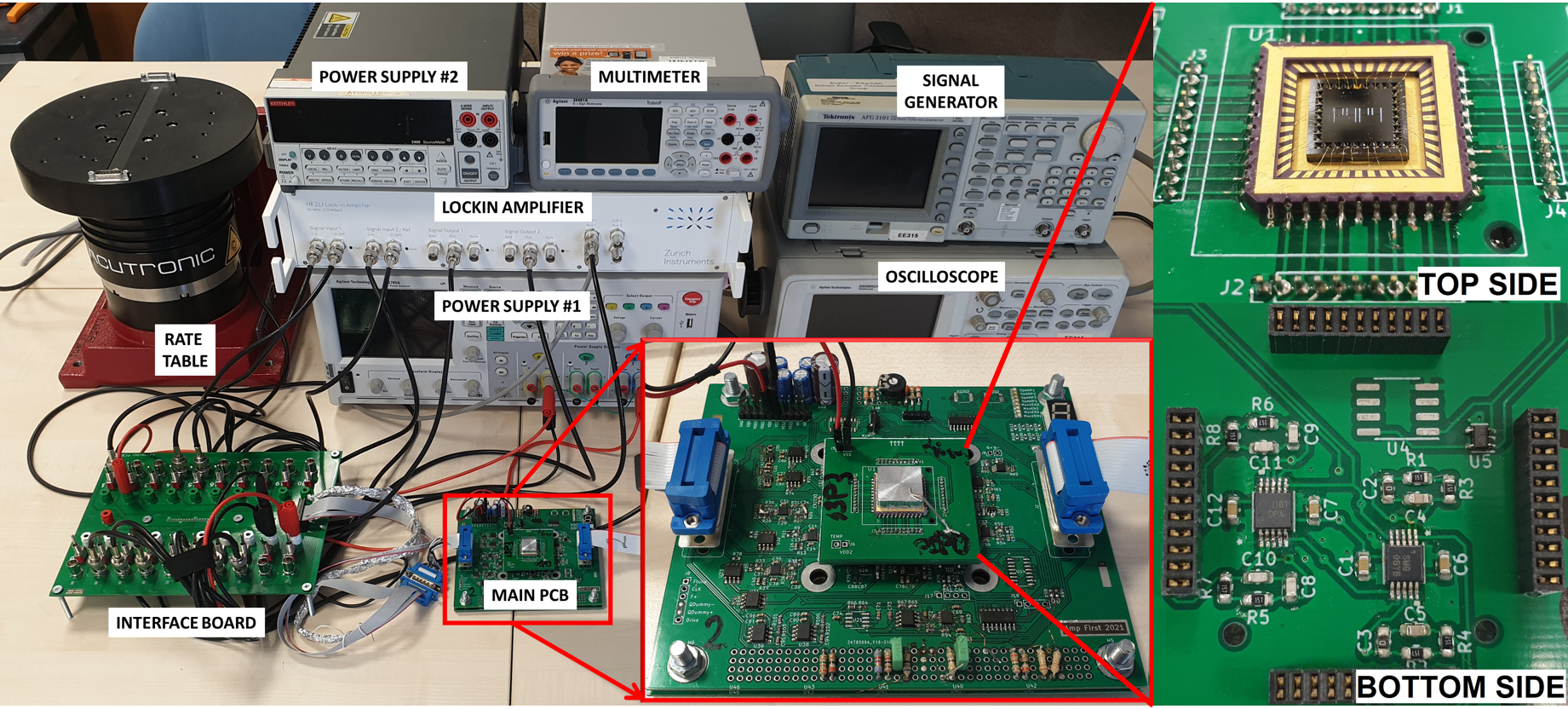
Below is a picture of the overall test setup when MEMS sensor and the electronics are connected. The system is quite complex, consisting of front end amplifiers, multiplexers for the stress sensor reading, signal conditioning amplifiers, multiple control loops, PLL,…
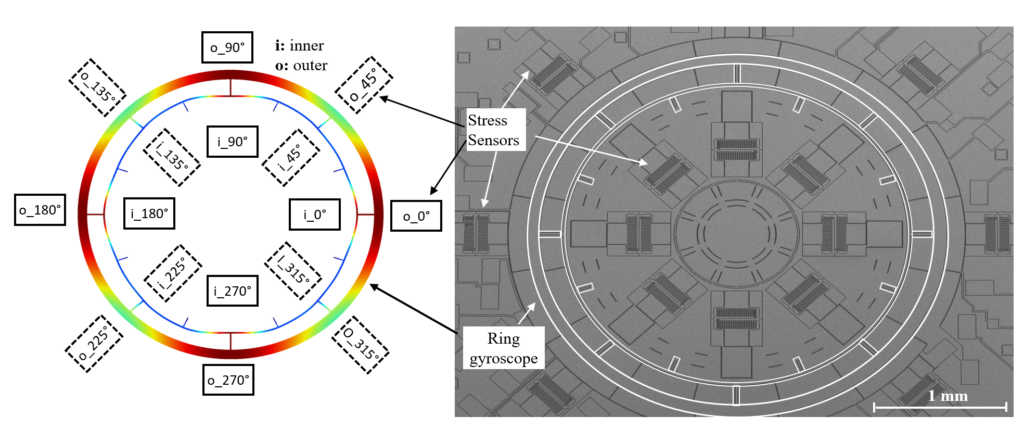
Stress Sensors
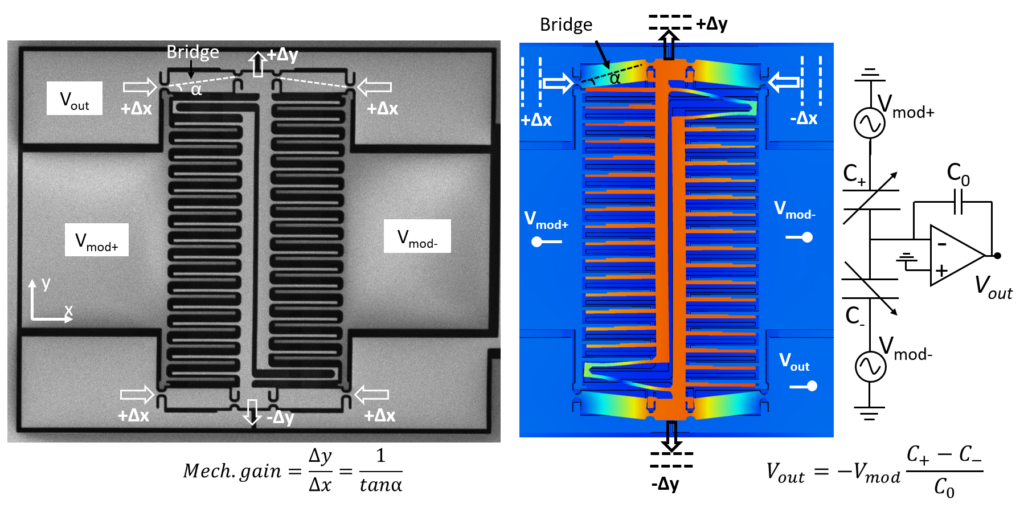
Stress could be measured using different ways. Metal foil strain gauges and piezoresistance are typical examples. We measure stress with capacitive stress sensors that amplify the substrate strain and convert it to capacitance.
Analytical Modeling
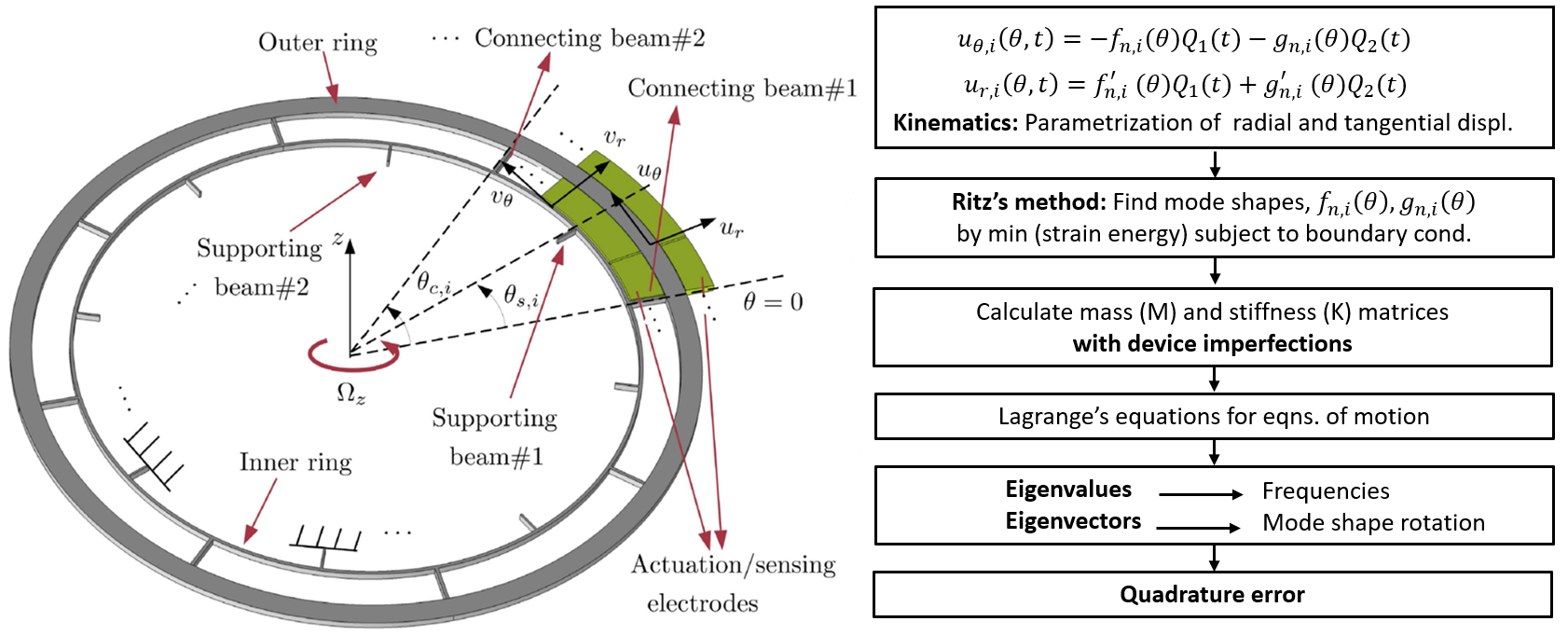
Analytical modeling enables deep understanding of the device operation in the presence of fabrication imperfections and stress. Full device operation could be implemented which is quite difficult with FEA (finite element analysis).
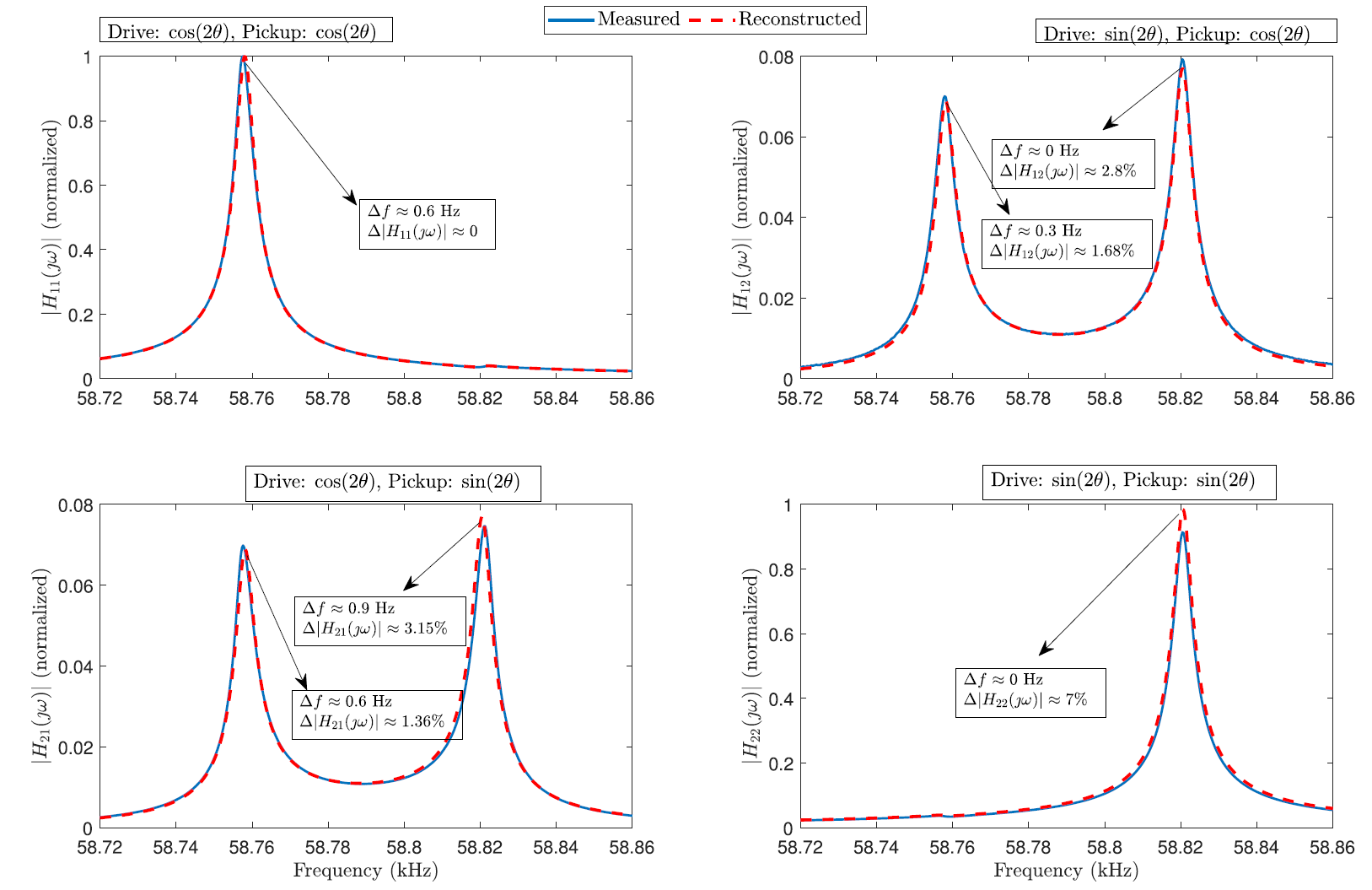
Below is the comparison of measured vs reconstructed frequency response of the gyroscope modes using the analytical model. There are two gyroscope modes and all the drive and pick off conditions are presented. The device imperfections (sidewall angles, width nonuniformities) lead to two peaks in the frequency response. The second peaks enables us to predict the device nonidealities.